 chromVAR inferring transcription-factor-associated accessibility from single-cell epigenomic data
chromVAR inferring transcription-factor-associated accessibility from single-cell epigenomic data
题目: chromVAR:从单细胞表观基因组数据推断转录因子相关的可及性
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4401 (opens new window)
Cite: Schep, A., Wu, B., Buenrostro, J. et al. chromVAR: inferring transcription-factor-associated accessibility from single-cell epigenomic data. Nat Methods 14, 975–978 (2017).
作者介绍:
| William J Greenleaf |
|---|
 |
| Department of Genetics, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, USA |
| wjg@stanford.edu |
# Abstract:
单细胞 ATAC-seq (scATAC) 产生的数据稀疏,这给传统分析带来了挑战。我们开发了 chromVAR http://www.github.com/GreenleafLab/chromVAR (opens new window),这是一个 R 包,用于通过估计共享相同motif或注释的peaks内可及性的增益或损失来分析稀疏染色质可及性数据,同时控制技术偏差。chromVAR 能够准确聚类 scATAC-seq 图谱,并表征与染色质可及性变化相关的已知和de novo sequence motifs。
# Main:
# Figure 1: chromVAR enables interpretable analysis of sparse chromatin-accessibility data.
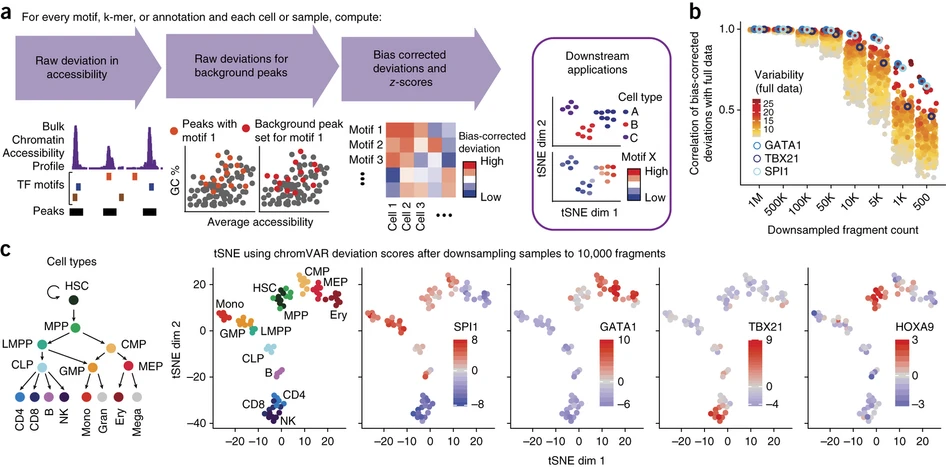
Figure 1. chromVAR 能够对稀疏染色质可及性数据进行可解释的分析
(a) chromVAR 聚合具有共同特征(例如 motif )的 peaks 上的染色质可及性,并应用偏差校正来生成可用于下游分析的每个细胞或样本的分数。
(b) 对来自不同造血群体的 77 个样本在对完整数据的总测序读数进行下采样之前和之后的偏倚校正偏差的 Pearson 相关性。
(c) 不同样品的 tSNE 可视化,使用根据每个样品下采样到 10,000 个片段(单个细胞的典型数量)的数据计算出的归一化偏差。
# Figure 2: chromVAR can be used to cluster single cells and interpret motifs underlying chromatin-accessibility variation.
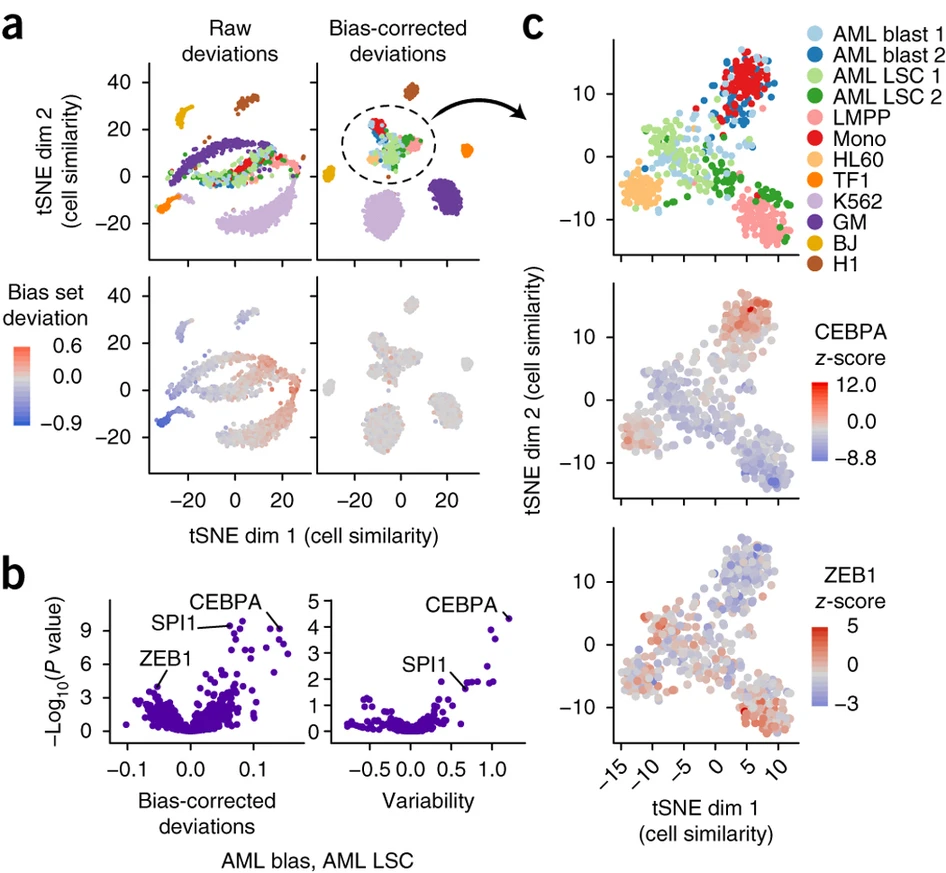
Figure 2. chromVAR 可用于对单细胞进行聚类并解释染色质可及性变异背后的 motif
(a) 基于 chromVAR 原始(左)或偏差校正偏差(右)的 1,561 个单细胞的 tSNE 可视化。
(b) 火山图显示 AML 母细胞 ( n = 122) 和 LSC 细胞 ( n = 144 ) 之间每个 motif 的偏差校正可及性偏差 (左) 和变异性 (右) 的平均差异。
(c) 不同簇中选定标记基因的基因得分的空间映射和选定基因的染色质可及性具有高度组织特异性。
# Figure 3: chromVAR identifies de novo motifs associated with chromatin-accessibility variation in single cells.
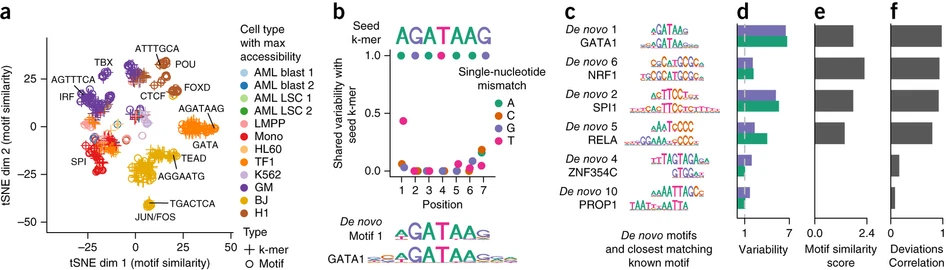
Figure 3. chromVAR从头识别与单细胞染色质可及性变异相关的 motif
(a) 基于细胞间标准化偏差向量的 motif 和 k-mers 之间相似性的 tSNE 可视化。
(b) 与种子 k-mer AGATAAG 存在一处不匹配的 k-mer 的共享变异性。
(c) chromVAR 使用七聚体偏差分数组装的de novo motif 示例,最接近的匹配已知 motif 紧接在下面。
(d) c中每对的de novo motif 和已知 motif 的变异性( z分数的 sd )。
(e) de novo motif 和c中已知 motif 之间的 motif 相似性评分。
(f) c中每对de novo motif 和已知 motif 的标准化偏差之间的 Pearson 相关性。
